- Table View
- List View
Concise Handbook of Fluorocarbon Gases: Applications in Refrigeration and Other Industries
by Sina EbnesajjadThis book describes fluorocarbons gases’ preparation process, properties, applications and their evolution over time. The impact of fluorocarbons on the ozone layer and global and the development to mitigate those effects have been specially emphasized. The first major industrial fluorinated compound was developed in the 1920’s, to replace ammonia and sulfur dioxide refrigerants, at the General Motors Frigidaire Division by Thomas Midgley, Jr. and Albert Leon Henne. They developed a family of fluorocarbons trademarked Freon® for auto air conditioning units revolutionizing the auto industry. Other applications were developed over time including fire extinguishers, propellants, blowing agents, cleaners, anesthesia, artificial blood and others impacting every facet of life. In spite of being in broad global use for nearly a century, fluorocarbon gases have gone through great evolution during the last few decades. In the 1980s it was discovered chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) gases are harmful to the ozone layer, mainly because of their chlorine content. Chlorine was released in the upper atmosphere when chlorofluorocarbon molecules were broken down by the high energy cosmic radiation. CFCs were progressively banned following the Montreal Protocol of 1987. CFCs were replaced by fluorinated gases containing either less chlorine (hydrofluoro-chlorocarbons, or HCFCs), which are much less damaging (about 90% less) to the ozone layer or with fluorinated gases containing no chlorine, i.e. hydrofluorocarbons or HFCs. HFC have no impact on the ozone layer but impact global warming detrimentally. HFCs are usable without need for changes to the existing refrigeration or air conditioning installations. More recently hydrofluoroolefins (HFOs), which have little or no negative impact on global warming, have been developed to replace or reduce the use of HFCs. HFOs are used as single compounds or in blends. Research and development continues to develop and replace the HCFCs and HFCs completely with environmentally friendly products. Concise Handbook of Fluorocarbon Gases presents a reference and text for the commercial fluorocarbon gases which have great many application in a wide range of industries such as refrigeration and air conditioning, as well as consumer products.
Concise Handbook of Mathematics and Physics
by Eugene I. Butikov Alexander S. Kondratyev Alexander G. AlenitsynConcise Handbook of Mathematics and Physics presents a unified and coherent treatment of all the major aspects of modern elementary physics and mathematics. This complete text/reference includes definitions of fundamental notations and physical and mathematical quantities, formulas that express the laws of physics, axioms and theorems of mathematics, and more. The information is organized logically (instead of alphabetically) for better comprehension and quick, convenient access.The book contains extensive cross-referencing between the mathematical and physical sections. reflecting the considerable overlap between these two areas of study and increasing the usefulness of this handbook. Fundamental concepts, theorems, and laws are demonstrated through numerous practical examples and tasks to help build problem-solving skills.
Concise Handbook of Psychoactive Herbs: Medicinal Herbs for Treating Psychological and Neurological Problems
by Marcello SpinellaFind out how plant-derived drugs react with your brain to produce either healing or harmful results!The Concise Handbook of Psychoactive Herbs will give you a better understanding of herbal products that have psychological effects. The book explores how they work, how effective they are, and what is known about their safety. Geared towards non-specialist professionals and curious individuals, this guide shows how herbal preparations can affect the brain, mental state, and behavior of a user and includes treatment methods, tables, illustrations, a glossary, and a bibliography.The Concise Handbook of Psychoactive Herbs contains chapters on several types of psychoactive herbs, including: stimulants cognition-enhancers sedatives painkillers hallucinogensWith the Concise Handbook of Psychoactive Herbs, you&’ll examine the effects of psychoactive drugs on the nervous system-both positive and negative. Each chapter discusses a type of herbal medicine, its action on the brain and other systems of the body, side effects, and the potential for addiction. The book closely examines possible drug interactions with prescription medications and emphasizes the caution you need to take when using herbal health products.In the Concise Handbook of Psychoactive Herbs you will learn about the psychoactive actions of such medicinal plants as: coffee tobacco cannabis ginseng chamomile cocoa opium poppy peyote gingko biloba
Concise Handbook of Waste Treatment Technologies
by Saleh S. Al Arni Mahmoud M. ElwaheidiWith specialized and succinct coverage, Concise Handbook of Waste Treatment Technologies provides readers with an integrated overview of various waste treatment technologies and related issues. Rather than dealing separately with each type of waste material, the book summarizes important waste treatments from a holistic perspective. Presents a comprehensive review of the most used terminologies and methods in waste management Explains how waste materials are treated and managed in a manner compatible with engineering, health, safety, and environmental regulations and laws Includes discussion of basic solid, liquid, and gaseous wastes Accessible to both specialists and non-specialists This guidebook is written for early career professionals, non-specialists, and specialists in environmental and chemical engineering and related disciplines seeking to understand proper waste and management and disposal techniques.
Concise History of Science and Invention: An Illustrated Time Line
by National GeographicFrom the ancient conquest of fire and the first turn of a wheel to the latest in scientific leaps toward the stars, this easy-access history offers a panoramic perspective on humankind's restless quest for the laws, theories, and tools by which we can grasp and master our universe. This concise, concentrated, consistently organized look at our species' key scientific and innovative achievements spans all human history, presenting ten distinct eras from the first glimmers of intelligence to the cutting-edge technologies of the modern world. Within these intuitive divisions, all human scientific endeavors and achievement are divided into four general fields of inquiry and arrayed into four basic geocultural regions for easy comparison in a logical, systematic grid format highlighted by 350 photographs, maps, illustrations, and diagrams that add graphic emphasis to key information. Special two-page feature spreads explore the most revolutionary developments in greater depth; compelling, expertly composed essays and memorable quotations add sparkle; and informative sidebars provide specifically focused items of information about particular inventions, ideas, or themes. Completing this comprehensive approach, an extensive glossary explains unfamiliar terms, and a detailed index makes it a simple matter to follow a particular field or process from its origin through its complete cross-cultural evolution. This is a reference as usefully accessible as it is inherently fascinating.
Concise Physical Chemistry
by Donald W. RogersThis book is a physical chemistry textbook that presents the essentials of physical chemistry as a logical sequence from its most modest beginning to contemporary research topics. Many books currently on the market focus on the problem sets with a cursory treatment of the conceptual background and theoretical material, whereas this book is concerned only with the conceptual development of the subject. Comprised of 19 chapters, the book will address ideal gas laws, real gases, the thermodynamics of simple systems, thermochemistry, entropy and the second law, the Gibbs free energy, equilibrium, statistical approaches to thermodynamics, the phase rule, chemical kinetics, liquids and solids, solution chemistry, conductivity, electrochemical cells, atomic theory, wave mechanics of simple systems, molecular orbital theory, experimental determination of molecular structure, and photochemistry and the theory of chemical kinetics.
Concise Textbook of Equine Clinical Practice Book 1: Lameness
by Antonio Cruz Graham Munroe Michael SchrammeThis concise, practical text covers the essential information veterinary students, new graduates and practitioners need to succeed in equine practice, focussing on lameness. Written for an international readership, the book conveys the core information in an easily digestible, precise form with extensive use of bullet-points, lists, diagrams, protocols and extensive illustration (over 650 full colour, high quality photographs). Part of a five-book series that extracts and updates key information from Munroe’s Equine Surgery, Reproduction and Medicine, Second Edition, the book distils best practice in a logical straightforward clinical-based approach. It details clinical anatomy, physical clinical examination techniques, diagnostic techniques and normal parameters, emphasising the things regularly available to general practitioners with minimal information of advanced techniques. The clinical information is split into anatomy-based sections. Ideal for veterinary students on clinical placements with horses as well as for practitioners needing a quick reference ‘on the ground’, the spiralbound format allows the book to lie open during practice.
Concise Textbook of Equine Clinical Practice Book 2: Reproduction and the Foal
by Victoria Scott Graham Munroe Tracey Chenier Charles D. CookeThis concise, practical text covers the essential information veterinary students and nurses, new graduates and practitioners need to succeed in equine practice, focussing on reproduction and the foal. Written for an international readership, the book conveys the core information in an easily digestible, precise form with extensive use of bullet-points, lists, diagrams, protocols and extensive illustrations (nearly 200 full colour, high quality photographs). Part of a five-book series that extracts and updates key information from Munroe’s Equine Surgery, Reproduction and Medicine, Second Edition, the book distils best practice in a logical straightforward clinical-based approach. It details clinical anatomy, physical clinical examination techniques, diagnostic techniques and normal parameters, emphasising the things regularly available to general practitioners with minimal information of advanced techniques. The clinical information is split into anatomy-based sections. Ideal for veterinary students and nurses on clinical placements with horses as well as for practitioners needing a quick reference ‘on the ground’.
Concise Textbook of Equine Clinical Practice Book 3: Respiratory and Gastrointestinal Diseases
by Graham Munroe Tim Barnett Laura H. JavsicasThis concise, practical text covers the essential information veterinary students and nurses, new graduates, and practitioners need to succeed in equine medicine, focussing on respiratory and gastrointestinal diseases. Written for an international readership, the book conveys the core information in an easily digestible, precise form with extensive use of bullet points, lists, diagrams, protocols, and extensive illustrations (over 300 full-colour, high-quality photographs). Part of a five-book series that extracts and updates key information from Munroe’s Equine Surgery, Reproduction and Medicine, Second Edition, the book distils best practice in a logical straightforward clinically based approach. It details relevant clinical anatomy, physical clinical examination techniques and findings, normal parameters, aetiology/pathophysiology, differential diagnoses, diagnostic techniques, management and treatment, and prognosis. The emphasis is on information tailored to general equine clinicians with just enough on advanced techniques to make the practitioner aware of what is available elsewhere. The respiratory system is split into sections on surgical and medical conditions of the upper and lower respiratory tracts. The gastrointestinal system is divided into the upper tract, including the oral cavity and dentistry, and the lower tract and peritoneal cavity. Ideal for veterinary students and nurses on clinical placements with horses as well as practitioners needing a quick reference ‘on the ground’.
Concise Textbook of Equine Clinical Practice Book 4: Liver, Endocrine, Urinary, Skin and Wounds
by Antonio Cruz François-René Bertin Andy Durham Derek KnottenbeltThis concise, practical text covers the essential information veterinary students need to succeed in equine medicine and surgery, focussing on skin, urinary, liver and endocrine diseases. Written for an international readership, the book conveys the core information in an easily digestible, precise form with extensive use of bullet points, tables, flow charts, diagrams, lists, protocols and extensive illustrations. Part of a five-book series that extracts and updates key information from Munroe’s Equine Surgery, Reproduction and Medicine, Second Edition, the book distils best practice in a logical straightforward clinical-based approach. It details clinical anatomy, physical clinical examination techniques, diagnostic techniques and normal parameters, emphasising the things regularly available to general practitioners with minimal information of advanced techniques. The liver section is divided into clinical evaluation, diagnostic tests, possible causes and treatment. The diagnostic approach to endocrine disease is followed by specific diseases of the thyroid, parathyroid, pituitary gland, equine metabolic syndrome and other miscellaneous disorders. The approach to urinary tract problems includes information on diagnostic tests and imaging, renal diseases,,and diseases of the ureter, bladder and urethra. The approach to skin disease is discussed in detail, including relevant diagnostic tests. Following this, individual skin diseases are covered under the headings of genetic, infectious, immune-mediated, nutritional, endocrine, idiopathic, traumatic and neoplastic causes. Finally, skin wounds, burns and infections of synovial structures are discussed. Ideal for veterinary students and nurses on clinical placements with horses as well as practitioners needing a quick reference ‘on the ground’.
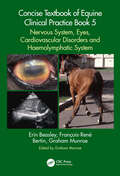
Concise Textbook of Equine Clinical Practice Book 5: Nervous System, Eyes, Cardiovascular Disorders and Haemolymphatic System
by Graham Munroe François-René Bertin Erin BeasleyThis concise, practical text covers the essential information veterinary students need to succeed in equine medicine and surgery, focusing on the nervous system, eyes, cardiovascular disorders and haemolymphatic systems. Written for an international readership, the book conveys the core information in an easily digestible, precise form with extensive use of bullet points, tables, flow charts, diagrams, lists, protocols and extensive illustrations. Part of a five-book series that extracts and updates key information from Munroe’s Equine Surgery, Reproduction and Medicine, Second Edition, the book distils best practice in a logical straightforward clinical-based approach. It details clinical anatomy, physical clinical examination techniques, diagnostic techniques and normal parameters, emphasising the things regularly available to general practitioners with minimal information of advanced techniques. The nervous system section discusses in detail the neurological exam, mentions relevant diagnostic tests and divides the diseases of the system into congenital, infectious, traumatic, toxin-induced and miscellaneous causes. In the eye section, the relevant anatomy and the examination of the eye are followed by discussion of useful diagnostic tests and procedures. Diseases of the eye are discussed under the headings of congenital/neonatal, neoplastic, infectious and inflammatory disorders, neurological based and parasitic problems. The cardiological examination and relevant diagnostic tests are followed by sections on arrhythmias, congenital and acquired cardiac diseases, pericardial disease and miscellaneous cardiovascular disease. Finally, the haemolymphatic section discusses in detail relevant diagnostic approaches and laboratory aids, followed by sections on anaemia, haemostasis disorders, infections and neoplasia. Ideal for veterinary students and nurses on clinical placements with horses, as well as practitioners needing a quick reference ‘on the ground’.
Concise Textbook of Large Animal Handling: A Practical Handbook
by C. B. ChastainThis concise instructional guide condenses the most important aspects of large animal handling. It provides a portable, durable, beside-the-animal means of learning, as well as a convenient way to refresh on how to strive for safety and efficacy in animal handling techniques. It is ideal for use during veterinary placements in all settings from farm to laboratory, to riding school. The text covers: • Handler safety • Animal safety • Sanitation • Approach and capture • Routine handling and release procedures • Handling for medical procedures • Use and supply sources of restraint equipment A Companion Website provides additional self-assessment questions and answers to aid learning. Important reading for undergraduate veterinary students on EMS rotations, as well as practicing veterinarians, technicians, and assistants, the book covers species encountered in farm, equine, and laboratory settings.
Concise Textbook of Small Animal Handling: A Practical Handbook
by C. B. ChastainThis instructional pocket reference condenses the most important aspects of small animal handling. It provides a portable, durable means of learning 'on the ground', as well as a convenient way to refresh on how to strive for safety and efficacy in animal handling techniques. Spiralbound for practical use at the animal’s side during veterinary placements in a clinic or laboratory, the text covers: Handler safety Animal safety Sanitation Approach and capture Routine handling and release procedures Handling for medical procedures Use and supply sources of restraint equipment A Companion Website provides additional self-assessment questions and answers to aid learning. Important reading for undergraduate veterinary students as well as practicing technicians, nurses and assistants, the book instructs on safe and humane handling of species encountered in both small animal practice and laboratory settings.
Concorde, A Designer's Life: The Journey to Mach 2
by Ted TalbotDo you remember the time we used to do New York in three hours?Even twenty years after its final flight, Concorde remains the pinnacle of aviation design. The aircraft is still unmatched, which has led to a vast swathe of material being written about the aeroplane itself. However, relatively little has been said about the people who designed it.Concorde, A Designer’s Life is an autobiography peppered with anecdotes from the team, humorous life stories and several ‘technibits’, all covering the design period of Concorde. Ted Talbot, who began his career at BAC as an aerodynamicist and later became chief design engineer, has combined the technical narrative with personal and family reminiscences to remind the reader that engineers have lives too.The path to Mach 2 was bumpy, with threats of cancellation and opposition from the Americans and the Russians, but this generally indicated to the Concorde team that they were on the right path! This informative, witty and thoroughly enjoyable peek into an unusual life is a valuable addition to any bookshelf.
Concorde: The thrilling account of history’s most extraordinary airliner
by Mike BannisterThe definitive account of the rise and fall of the iconic Concorde plane from British Airways' former Chief Concorde Pilot'A remarkable story' DAILY EXPRESS'A stonking good read' FLYER_________What's it like to fly faster than a bullet?Could you really glimpse the edge of space?Why will we never see Concorde's like again?Mike Bannister was British Airways' Chief Concorde Pilot. One of the few in that legendary aircraft's quarter-century of flight to fully understand both the plane's intricate engineering and what it took to fly her at supersonic speeds.In this definitive account of the rise and fall of the world's greatest aircraft, Bannister explores its origins, development, service, highs, lows and, finally, the terrible crash which ended its flying life.Part celebration, part history, part detective story and part courtroom drama, it's almost as riveting as flying in Concorde itself - almost . . ._________'Concorde represented the sheer wondrous genius of the human race' JEREMY CLARKSON
Concrete Durability and Service Life Planning: Proceedings of ConcreteLife’20 (RILEM Bookseries #26)
by Konstantin Kovler Semion Zhutovsky Sabrina Spatari Ole M. JensenThis volume gathers the proceedings of the 3rd International RILEM Workshop on Concrete Durability and Service Life Planning (ConcreteLife’20), held in Haifa, Israel in January 2020. The papers cover a range of topics in concrete curing, cracking in concrete structures, corrosion of steel in concrete, thermal and hygral effects, concrete in cold climates and under high temperatures, recycling, alkali-silica reactions, chloride and sulfate attacks, marine structures, transport phenomena, durability design, microstructure of concrete and volume changes, and life cycle assessment. The book also explores future trends in research, development, and practical engineering applications related to durable concrete construction, and focuses on the design and construction of concrete structures exposed to various environmental conditions and mechanical loading. Given its scope, it offers a valuable asset for all researchers and graduate students in the areas of cement chemistry, cement production, and concrete design.
Concrete Fracture Models and Applications
by Sudhirkumar V Barai Shailendra KumarCementitious materials, rocks and fibre-reinforced composites commonly termed as quasibrittle, need a different fracture mechanics approach to model the crack propagation study because of the presence of significant size of fracture process zone ahead of the crack-tip. Recent studies show that concrete structures manifest three important stages in fracture process: crack initiation, stable crack propagation and unstable fracture or failure. Fracture Mechanics concept can better explain the above various stages including the concepts of ductility, size-effect, strain softening and post-cracking behavior of concrete and concrete structures. The book presents a basic introduction on the various nonlinear concrete fracture models considering the respective fracture parameters. To this end, a thorough state-of-the-art review on various aspects of the material behavior and development of different concrete fracture models is presented. The development of cohesive crack model for standard test geometries using commonly used softening functions is shown and extensive studies on the behavior of cohesive crack fracture parameters are also carried out. The subsequent chapter contains the extensive study on the double-K and double-G fracture parameters in which some recent developments on the related fracture parameters are illustrated including introduction of weight function method to Double-K Fracture Model and formulization of size-effect behavior of the double-K fracture parameters. The application of weight function approach for determining of the KR-curve associated with cohesive stress distribution in the fracture process zone is also presented. Available test data are used to validate the new approach. Further, effect of specimen geometry, loading condition, size-effect and softening function on various fracture parameters is investigated. Towards the end, a comparative study between different fracture parameters obtained from various models is presented.
Concrete Planet: The Strange and Fascinating Story of the World's Most Common Man-Made Material
by Dennis Smith Robert CourlandConcrete: We use it for our buildings, bridges, dams, and roads. We walk on it, drive on it, and many of us live and work within its walls. But very few of us know what it is. We take for granted this ubiquitous substance, which both literally and figuratively comprises much of modern civilization's constructed environment; yet the story of its creation and development features a cast of fascinating characters and remarkable historical episodes. This book delves into this history, opening readers' eyes at every turn.In a lively narrative peppered with intriguing details, author Robert Corland describes how some of the most famous personalities of history became involved in the development and use of concrete--including King Herod the Great of Judea, the Roman emperor Hadrian, Thomas Edison (who once owned the largest concrete cement plant in the world), and architect Frank Lloyd Wright. Courland points to recent archaeological evidence suggesting that the discovery of concrete directly led to the Neolithic Revolution and the rise of the earliest civilizations. Much later, the Romans reached extraordinarily high standards for concrete production, showcasing their achievement in iconic buildings like the Coliseum and the Pantheon. Amazingly, with the fall of the Roman Empire, the secrets of concrete manufacturing were lost for over a millennium. The author explains that when concrete was rediscovered in the late eighteenth century it was initially viewed as an interesting novelty or, at best, a specialized building material suitable only for a narrow range of applications. It was only toward the end of the nineteenth century that the use of concrete exploded. During this rapid expansion, industry lobbyists tried to disguise the fact that modern concrete had certain defects and critical shortcomings. It is now recognized that modern concrete, unlike its Roman predecessor, gradually disintegrates with age. Compounding this problem is another distressing fact: the manufacture of concrete cement is a major contributor to global warming. Concrete Planet is filled with incredible stories, fascinating characters, surprising facts, and an array of intriguing insights into the building material that forms the basis of the infrastructure on which we depend.From the Hardcover edition.
Concrete Structures in Earthquake
by Thomas T. C. HsuThis book gathers 23 papers by top experts from 11 countries, presented at the 3rd Houston International Forum: Concrete Structures in Earthquake. Designing infrastructures to resist earthquakes has always been the focus and mission of scientists and engineers located in tectonically active regions, especially around the “Pacific Rim of Fire” including China, Japan, and the USA. The pace of research and innovation has accelerated in the past three decades, reflecting the need to mitigate the risk of severe damage to interconnected infrastructures, and to facilitate the incorporation of high-speed computers and the internet. The respective papers focus on the design and analysis of concrete structures subjected to earthquakes, advance the state of knowledge in disaster mitigation, and address the safety of infrastructures in general.
Concrete and Clay: Reworking Nature in New York City (Urban and Industrial Environments)
by Matthew GandyAn interdisciplinary account of the environmental history and changing landscape of New York City. In this innovative account of the urbanization of nature in New York City, Matthew Gandy explores how the raw materials of nature have been reworked to produce a "metropolitan nature" distinct from the forms of nature experienced by early settlers. The book traces five broad developments: the expansion and redefinition of public space, the construction of landscaped highways, the creation of a modern water supply system, the radical environmental politics of the barrio in the late 1960s and early 1970s, and the contemporary politics of the environmental justice movement. Drawing on political economy, environmental studies, social theory, cultural theory, and architecture, Gandy shows how New York's environmental history is bound up not only with the upstate landscapes that stretch beyond the city's political boundaries but also with more distant places that reflect the nation's colonial and imperial legacies. Using the shifting meaning of nature under urbanization as a framework, he looks at how modern nature has been produced through interrelated transformations ranging from new water technologies to changing fashions in landscape design. Throughout, he considers the economic and ideological forces that underlie phenomena as diverse as the location of parks and the social stigma of dirty neighborhoods.
Concrete and Mortar Production using Stone Siftings
by Leonid Dvorkin Vadim Zhitkovsky Yuri RibakovThe monograph analyses the state of the art (problem) in using stone siftings and aspiration dust obtained in natural stone crushing for producing concrete aggregates and fillers for dry construction mixtures and mortars on their basis. The influence of disperse fraction in stone siftings and aspiration dust on structural, mechanical and rheological properties of cement composite construction materials is investigated. Hypothesis for obtaining technological conditions, providing positive effect of the disperse fraction on strength and other properties of cement based concrete and mortar is proposed. <P><P> Experimental results on studying properties of dry mixtures and mortars on their basis using stone crushing aspiration dust as filler are presented. Efficiency of using fillers, based on igneous rocks, on adhesive and other properties of mortars is demonstrated. Methodology for design of mortars composition for given mortar properties in case, when aspiration dust is used as filler, is proposed. <P><P> The monograph presents experimental results on fine-grained concrete including as a main filler stone siftings with up to 20% of disperse fraction. It is shown that it is possible to produce fine grain concrete class С20/25…С60/75. Technological parameters of vibro-pressed fine-grained concrete with raw stone siftings are developed. Methodologies for composition design of fine-grained concrete with given workability are proposed. Possibility for producing macroporous light-weight concrete for walls and filtration materials, based on stone siftings fillers is shown.
Concrete-Filled Steel Tubular Arch Bridges
by Baochun Chen Junping Liu Jiangang WeiThis book discusses the features of composite materials and arch structures. Providing an in-depth fundamental and practical guide to the field, it systemically addresses all aspects of concrete-filled steel tubular (CFST) arch bridges, including a comprehensive overview on technical developments, structural systems, structural detailing, design and analysis, construction technology, and maintenance. The real-world examples presented have been carefully selected to highlight the advanced theoretical and technological solutions for CFST arch bridges and to motivate researchers to promote innovative and sustainable development in the area. The book couples fundamental concepts with advanced practices translated from the third edition of the author’s Chinese book on CFST arch bridges, which has been the most significant book on the topic since the first edition published in 1999. This English translation can servers as an idea textbook for postgraduate students in the fields of civil, construction and environmental engineering, especially in bridge engineering, as well as a perfect review and reference guide for engineering practitioners and researchers.
Concrete Reinforcement Degradation and Rehabilitation: Damages, Corrosion and Prevention (Engineering Materials)
by Yuli Panca AsmaraThis book provides an overview of various methods of concrete reinforcement against corrosion. It consists of chapters, discussing reinforced concrete, concrete damages, causes of damages, protection, concrete maintenance, principles of corrosion, and how to conduct experiments to obtain reinforced concrete data. This book contributes to the infrastructure industry and is useful for the wider community to add insight into the field of corrosion and material damage. Reinforced concrete is a construction material that combines concrete and steel reinforcement. Thus, studying corrosion is useful for knowing when a material will break down and what will happen to the metal now and in the future. Knowing the corrosion process will prevent sudden damage, so it can provide early preparation. For this reason, knowledge is needed on how to check for damage to concrete, the process of corrosion mechanisms, corrosion prevention, methods for calculating corrosion rates, and how to maintain reinforced concrete so that it lasts longer. This book caters to researchers, administrators, academicians, policymakers, entrepreneurs, practitioners, instructors, and students who are looking to enrich their understanding of concrete reinforcement against corrosion.
Concussion
by Jeanne Marie Laskas<P>Soon to be a major motion picture starring Will Smith, Concussion is the riveting, unlikely story of Dr. Bennet Omalu, the pathologist who made one of the most significant medical discoveries of the twenty-first century, a discovery that challenges the existence of America's favorite sport and puts Omalu in the crosshairs of football's most powerful corporation: the NFL. <P>Jeanne Marie Laskas first met the young forensic pathologist Dr. Bennet Omalu in 2009, while reporting a story for GQ that would go on to inspire the movie Concussion. Omalu told her about a day in September 2002, when, in a dingy morgue in downtown Pittsburgh, he picked up a scalpel and made a discovery that would rattle America in ways he'd never intended. <P>Omalu was new to America, chasing the dream, a deeply spiritual man escaping the wounds of civil war in Nigeria. The body on the slab in front of him belonged to a fifty-year-old named Mike Webster, aka "Iron Mike," a Hall of Fame center for the Pittsburgh Steelers, one of the greatest ever to play the game. After retiring in 1990, Webster had suffered a dizzyingly steep decline. Toward the end of his life, he was living out of his van, tasering himself to relieve his chronic pain, and fixing his rotting teeth with Super Glue. <P>How did this happen?, Omalu asked himself. How did a young man like Mike Webster end up like this? The search for answers would change Omalu's life forever and put him in the crosshairs of one of the most powerful corporations in America: the National Football League. <P>What Omalu discovered in Webster's brain--proof that Iron Mike's mental deterioration was no accident but a disease caused by blows to the head that could affect everyone playing the game--was the one truth the NFL wanted to ignore. <P> Taut, gripping, and gorgeously told, Concussion is the stirring story of one unlikely man's decision to stand up to a multibillion-dollar colossus, and to tell the world the truth. <P><b>A New York Times Bestseller</b>
Concussive Brain Trauma: Neurobehavioral Impairment & Maladaptation, Second Edition
by Rolland S. ParkerFocusing on a public health problem affecting millions of people of all ages, the second edition of Concussive Brain Trauma: Neurobehavioral Impairment and Maladaptation reflects Dr. Rolland S. Parker's more than 25 years of neuropsychological practice and research in traumatic brain injury and stress, and his prior experience as a clinical psychol